Gauhati University Corporate Accounting Solved Question Paper 2023:
COMMERCE (HONOURS)
Paper: COM-HC-2016
(CORPORATE ACCOUNTING)
Full Marks: 80
Time: Three hours
The figures in the margin indicate full marks for the questions.
1.(1) Fill in the blanks with appropriate word/words: (any five) 1x5=5
(a) Schedule III of the companies Act, 2013 is related to the form and contents of the Balance Sheet and Statement of Profit & Loss.
(b) Capital redemption reserve can be utilized for issuing fully paid bonus shares.
(c) The debt-equity ratio after the buy-back of shares should not exceed 2:1.
(d) The Accounting standard AS-14 deals with accounting for amalgamation.
(e) Pooling of interest method of accounting is applied in case of amalgamation in the nature of merger.
(f) Post-acquisition profits are treated as revenue profits.
(g) Reduction of share capital requires a section by court.
(2) State whether the following statements are true or false: (any five): 1 x 5=5
(a) Interim dividend is declared between two Annual General Meetings.
True
(b) The right to apply for Right Shares is optional.
True
(c) At the time of valuation of Goodwill, only operating profit is taken into consideration.
False
(d) Buy-back of shares does not affect the authorized share capital of a company.
True
(e) Accounting standard 12 is related to accounting for holding companies.
False
(f) All the assets and liabilities of the transferor company become the assets and liabilities of the transferee company when the amalgamation is in the nature of purchase.
True
(g) A subsidiary company cannot buy shares of the holding company after it becomes its subsidiary.
False
(h) Goodwill is a non-current asset.
True
2. Answer the following: (any five) 2 x 5=10
(a) Mention any four components of financial statements of a company.
(b) What is the treatment of preliminary expenses while preparing final accounts of companies?
(c) What is capitalisation of reserve?
(d) What is Escrow Account?
(e) Write two methods of valuation of equity shares.
(f) Write two methods for calculating purchase consideration.
(g) What is consolidated Balance Sheet?
(h) What is meant by pre-acquisition profit?
ANSWERS:
(a) Four components of financial statements of a company are:
Balance Sheet: A statement that presents the financial position of the company at a specific point in time.
Profit and Loss Account: A statement that shows the revenue, expenses, and profit or loss of the company for a specific period.
Cash Flow Statement: A statement that shows the inflow and outflow of cash and cash equivalents of the company during a specific period.
Notes to Accounts: A section that provides additional information about the financial statements, including the accounting policies and assumptions used, and any other relevant disclosures.
(b) Preliminary expenses are expenses incurred in connection with the incorporation of a company, such as registration fees, legal fees, and printing costs. These expenses are treated as an asset and are shown in the balance sheet under the head "Miscellaneous Expenditure." They are written off over a period of time (not exceeding five years) out of the profits of the company.
(c) Capitalisation of reserve refers to the process of using the company's reserves to issue bonus shares to its shareholders. This is done by converting the accumulated profits or reserves of the company into equity shares.
(d) An Escrow Account is a temporary holding account created by a third-party intermediary, usually a lawyer or bank, to hold funds or assets on behalf of two or more parties in a transaction. The account acts as a safety net, ensuring that the assets or funds are not released until all parties have met the conditions of the agreement.
(e) Two methods of valuation of equity shares are:
Net Asset Value (NAV) Method: This method calculates the value of equity shares based on the net assets of the company, i.e., the total assets minus the total liabilities. The net assets are then divided by the total number of equity shares to arrive at the value per share.
Price Earnings (P/E) Ratio Method: This method calculates the value of equity shares based on the market price of the shares and the earnings per share (EPS) of the company. The market price per share is divided by the EPS to arrive at the P/E ratio. The P/E ratio is then applied to the EPS to arrive at the value per share.
(f) Two methods for calculating purchase consideration are:
1.Net Assets Method: In this method, the purchase consideration is calculated by subtracting the value of net assets acquired from the total purchase price paid.
2.Earnings Multiplier Method: In this method, the purchase consideration is calculated by multiplying the earnings of the acquired company by a predetermined multiple.
(g) A Consolidated Balance Sheet is a financial statement that combines the financial information of a parent company and its subsidiaries. It shows the financial position of the entire group as if it were a single entity.
(h) Pre-acquisition profit refers to the profit earned by a subsidiary company before it is acquired by the parent company. This profit belongs to the subsidiary company and is not available to the parent company. It is shown as a separate item in the consolidated balance sheet.
3. Answer any four of the following: 5 x 4=20
(a) Write any five differences between Right Shares and Bonus Shares.
Ans: The five differences between Right Shares and Bonus Shares are:
a).Definition: Right Shares are the shares issued to the existing shareholders of a company in proportion to their current shareholding, giving them the right but not the obligation to purchase additional shares. Bonus Shares, on the other hand, are shares issued to the existing shareholders of a company free of cost, as a reward for their investment.
b).Purpose: Right Shares are issued to raise additional capital for the company, whereas Bonus Shares are issued to capitalize on the accumulated profits or reserves of the company.
c).Price: Right Shares are issued at a price that is generally lower than the prevailing market price, whereas Bonus Shares are issued at no cost to the shareholders.
d).Dilution: Right Shares lead to dilution of ownership for existing shareholders, as their percentage ownership decreases if they do not exercise their right to purchase additional shares. Bonus Shares, however, do not result in any dilution of ownership for existing shareholders, as their percentage ownership remains the same.
e).Taxation: Right Shares are taxable as capital gains when they are sold, whereas Bonus Shares are not taxable, as they are issued free of cost.
(b) Pragati Ltd. has a capital of Rs. 9,00,000 divided into 90,000 equity shares of Rs. 10 each fully paid up. The company decided to return Rs. 3 per share to equity shareholders and make the shares Rs. 7 called up and paid up. Pass journal entries in the books of the company.
Ans: To return Rs. 3 per share, the company will make a payment of Rs. 2,70,000 (90,000 shares x Rs. 3 per share). The new called up and paid up value will be Rs. 7 per share, which means the company will call up an additional Rs. 4 per share (Rs. 10 par value - Rs. 7 called up value). The journal entries to be passed in the books of Pragati Ltd. are as follows:
In the books of Pragati Ltd.
Journal Entries
(c) The following is the extract of Trial Balance of Star Ltd. as on 31-03-2022.
You are required to prepare a Statement of Profit & Loss after considering the following:
(1) Closing stock as on 31/03/2022 is Rs. 20,000.
(2) Depreciate machinery @ 10% p.a. for 6 months.
(d) How will the following items be shown while preparing the final accounts of a company?
(1) Unclaimed dividend.
(2) Proposed dividend.
Ans:
(1) Unclaimed Dividend:
Unclaimed dividend is the amount of dividend declared by a company but not yet claimed by the shareholders. The final accounts of the company will show the unclaimed dividend as a current liability under the head 'Current Liabilities and Provisions' until the shareholders claim it. Once the dividend is claimed by the shareholders, it will be transferred to the 'Reserves and Surplus' account as a transfer to the general reserve.
(2) Proposed Dividend:
Proposed dividend is the amount of dividend that a company proposes to pay to its shareholders but has not yet been approved by the shareholders in the Annual General Meeting. The proposed dividend is shown in the final accounts of the company as a current liability under the head 'Current Liabilities and Provisions' until it is approved by the shareholders in the AGM. Once the proposed dividend is approved by the shareholders, it is transferred to the 'Provision for Dividend' account.
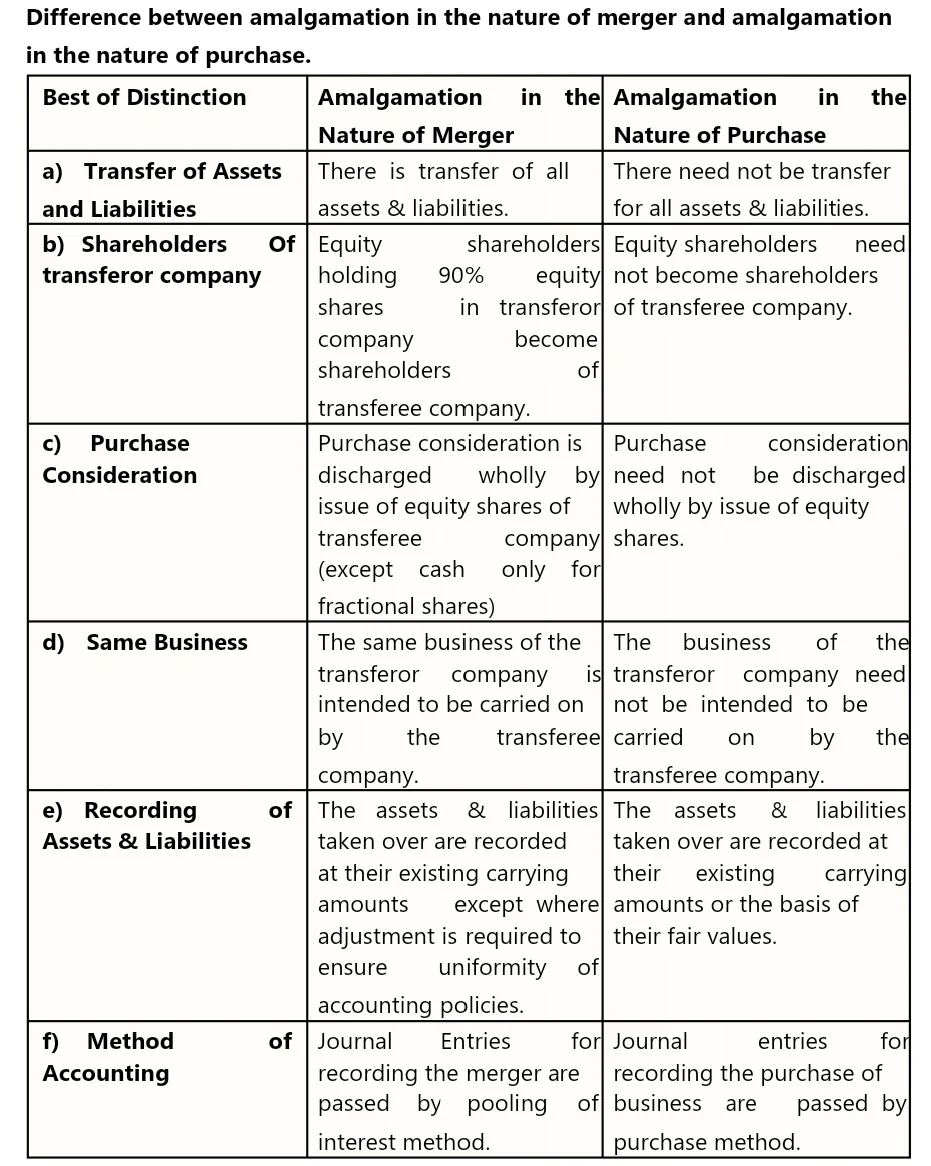
(e) Write any five differences between Amalgamation in the nature of Merger and Amalgamation in the nature of Purchase.
Ans:
(f) How is minority interest computed in case of a holding company?
Ans: In the case of a holding company, minority interest refers to the portion of the net assets of a subsidiary that is not owned by the holding company. Minority interest is calculated as the proportionate share of the net assets and profits of the subsidiary that is not owned by the holding company.
To compute minority interest, the following steps are taken:
Determine the subsidiary's net assets.
Deduct the portion of net assets that belong to the holding company.
The remaining net assets represent the portion of net assets belonging to the minority interest.
Calculate the proportionate share of the subsidiary's profits that belongs to the minority interest.
The minority interest is usually presented as a separate line item in the consolidated balance sheet and consolidated statement of profit and loss of the holding company. The purpose of disclosing minority interest is to provide a clear and transparent picture of the ownership structure of the subsidiary and the holding company's economic interest in the subsidiary.
(g) What is the need for consolidated financial statements in case of a holding company?
Ans: Consolidated financial statements are necessary in the case of a holding company because they provide a complete picture of the financial position, performance, and cash flows of the group as a whole, including the holding company and its subsidiaries. This is important for various stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and regulatory authorities who need to make informed decisions based on the overall financial health of the group. Consolidated financial statements also eliminate inter-company transactions and balances, giving a true and fair view of the group's financial performance and position.
(h) From the following information, calculate the value of Goodwill under 4 years purchase of super profit:
(1) Net profit for last 4 years – Rs. 30,000, Rs. 40,000, Rs. 50,000 and Rs. 60,000.
(2) The net profit includes non-operating profit on an average Rs. 3,000 p.a.
(3) Average capital employed Rs. 3,00,000.
(4) Normal rate of return 10%.
Ans: To calculate the value of Goodwill, we need to determine the super profits earned by the company in the last four years.
Step 1: Calculate the average net profit earned by the company over the last four years, excluding the non-operating profit:
Average net profit = (30,000 + 40,000 + 50,000 + 60,000) / 4 = Rs. 45,000
Step 2: Add the non-operating profit to the average net profit:
Adjusted average net profit = 45,000 + 3,000 = Rs. 48,000
Step 3: Calculate the normal rate of return on the capital employed:
Normal rate of return = 10% of Rs. 3,00,000 = Rs. 30,000
Step 4: Calculate the super profit earned by the company:
Super profit = Adjusted average net profit - Normal rate of return = Rs. 48,000 - Rs. 30,000 = Rs. 18,000
Step 5: Calculate the value of Goodwill using the 4 years purchase method:
Value of Goodwill = Super profit x Number of years' purchase
Number of years' purchase = 4
Value of Goodwill = Rs. 18,000 x 4 = Rs. 72,000
Therefore, the value of Goodwill under 4 years purchase of super profit is Rs. 72,000.
---------------------------------------------
For Complete Solution of Corporate Accounting (Only Theory) Question Paper 2022 Download PDF File 👇
DEMO PDF
---------------------------------------------
4. Answer any four from the following questions: 10 x 4=40
(1) What is buy-back of shares? Moon Ltd. has share capital of Rs. 5,00,000 in equity shares of Rs. 10 each. It has Rs. 3,00,000 in general reserve and Rs. 60,000 in Security Premium Account. The company in a special resolution decided to buy-back 10,000 equity shares at par out of its free reserves. Total liabilities of the company amounted to Rs. 9,00,000.
Pass journal entries in the books of the company and show necessary workings. 2+8=10
Ans: Buy-back of shares refers to the process by which a company buys back its own shares from its shareholders. This can be done either by purchasing shares on the open market or by offering to buy them back directly from shareholders. The purpose of a share buyback can vary, but it is often done to return excess cash to shareholders or to improve the company's financial ratios.
a) To transfer the required amount from General Reserve to Capital Redemption Reserve:
General Reserve A/c Dr. = Rs. 1,00,000
To Capital Redemption Reserve A/c = Rs. 1,00,000
b) To transfer the required amount from Security Premium Account to Capital Redemption Reserve:
Security Premium Account A/c Dr. = Rs. 10,000
To Capital Redemption Reserve A/c = Rs. 10,000
c) To record the buyback of shares at par:
Equity Share Capital A/c Dr. = Rs. 1,00,000
Capital Redemption Reserve A/c Dr. = Rs. 20,000
To Bank A/c = Rs. 1,20,000
(10,000 shares x Rs. 10 per share = Rs. 1,00,000)
(20,000 for the transfer of Rs. 1,00,000 from General Reserve and Rs. 10,000 from Security Premium Account)
Working:
Total Free Reserves = General Reserve + Security Premium Account
= Rs. 3,00,000 + Rs. 60,000
= Rs. 3,60,000
Maximum Buyback = 25% of Paid Up Capital + Free Reserves
= 25% of Rs. 5,00,000 + Rs. 3,60,000
= Rs. 2,35,000
Since the buyback amount is only Rs. 1,20,000, it is within the permissible limit of the maximum buyback amount.
Total Liabilities = Rs. 9,00,000
Paid Up Capital = Rs. 5,00,000
Free Reserves = Rs. 3,60,000
Therefore, the company can buy back up to Rs. 2,35,000 worth of shares. As the buyback amount is only Rs. 1,20,000, it is within the permissible limit.
(2) What is meant by valuation of share? Explain the need for valuation of share. 2+8=10
Ans:Valuation of share refers to the process of determining the fair market value of a company's shares. This is done by analyzing various factors such as the company's financial performance, future growth prospects, industry trends, and market conditions.
The need for valuation of shares arises for various reasons such as:
1.Buying or selling shares: When buying or selling shares in a company, it is important to know the fair market value of the shares to ensure that the price paid or received is reasonable.
2.Raising capital: Companies may need to raise capital by issuing new shares. In such cases, it is important to determine the fair market value of the shares to ensure that they are priced appropriately.
3.Mergers and acquisitions: Valuation of shares is essential in mergers and acquisitions to determine the fair exchange ratio between the companies involved.
4.Financial reporting: Companies need to report the value of their shares in their financial statements. Valuation of shares helps companies to accurately report their financial performance and position.
5.Litigation: In cases of disputes such as shareholder disputes, divorce, or bankruptcy, valuation of shares is necessary to determine the fair value of the shares for settlement purposes.
In summary, valuation of shares is a critical aspect of the financial decision-making process for companies, investors, and other stakeholders. It helps to determine the true value of a company's shares and ensures that all parties involved are fairly compensated.
(3) What is Internal Reconstruction? Mention the situations which call for internal reconstruction of a company. Discuss any one method of reduction of share capital. 2+4+4=10
Ans:Internal Reconstruction refers to the process by which a company reorganizes its financial structure without being liquidated. It involves altering the company's capital structure, operations, and assets to improve its financial position.
The following are the situations that call for internal reconstruction of a company:
Accumulated losses: When a company has incurred significant losses over time, and its financial position has deteriorated, internal reconstruction may be necessary to restore the company's financial health.
Excessive capital: When a company has more capital than it needs to operate efficiently, internal reconstruction may be required to reduce its capital base and optimize its operations.
Change in business strategy: When a company changes its business strategy or focus, it may require internal reconstruction to align its operations with its new strategy.
Change in the regulatory environment: Changes in the regulatory environment may require companies to reorganize their operations or capital structure to comply with new regulations.
One method of reducing share capital in internal reconstruction is by cancelling or reducing the nominal value of shares. The following is the process for reducing share capital through this method:
Obtain approval: The company must obtain approval from the shareholders and the court to reduce the share capital.
Create a reserve: A reserve equal to the amount of the reduction in share capital must be created to protect the creditors' interests.
Cancel or reduce shares: The company can cancel or reduce the nominal value of the shares by passing a special resolution and amending the company's memorandum of association.
File necessary documents: The company must file the necessary documents with the registrar of companies, such as the notice of reduction, special resolution, and the amended memorandum of association.
By reducing the share capital, the company can improve its financial position by eliminating accumulated losses, reducing its capital base, and optimizing its operations.
Gauhati University Bcom 2nd Sem Corporate Accounting Solved Question Paper 2022
(4) Explain the legal provisions under companies Act, 2013 regarding preparation of financial statements. 10
Ans: The Companies Act, 2013 sets out the legal provisions for the preparation of financial statements by companies. The financial statements provide an overview of the company's financial performance and position, and are used by various stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and regulatory authorities. The key provisions regarding the preparation of financial statements are as follows:
1.Applicable accounting standards: The financial statements must be prepared in accordance with the applicable accounting standards notified by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
2.True and fair view: The financial statements must present a true and fair view of the company's financial performance and position. The directors are responsible for ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the financial statements.
3.Consolidation of financial statements: If a company has one or more subsidiaries, it must prepare consolidated financial statements that include the financial performance and position of the company and its subsidiaries.
4.Board's report: The directors must prepare a board's report that provides a comprehensive analysis of the company's financial performance and position, and discloses any significant events or transactions that have occurred during the year.
5.Auditor's report: The financial statements must be audited by a qualified auditor who will issue an auditor's report. The auditor's report must provide an opinion on whether the financial statements present a true and fair view of the company's financial performance and position.
6.Filing of financial statements: The financial statements, board's report, and auditor's report must be filed with the Registrar of Companies within 30 days of the annual general meeting.
7.Compliance with Indian Accounting Standards: The financial statements must comply with the Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) notified by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
8.Adoption of accounting policies: The company must adopt and disclose appropriate accounting policies that are consistent with the accounting standards and provide a true and fair view of the company's financial performance and position.
8.Use of accrual basis of accounting: The financial statements must be prepared on the accrual basis of accounting, which means that income and expenses must be recognized when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid.
9.Disclosure of related party transactions: The financial statements must disclose any related party transactions entered into by the company during the year and the nature of the relationships between the parties involved.
Gauhati University Bcom 2nd Sem Corporate Accounting Solved Question Paper 2022
(5) Sky Ltd. resolved to utilize Rs. 4,00,000 out of its General Reserve balance to declare a bonus to shareholders by paying the final call of Rs. 4 per share on 1,00,000 shares of Rs. 10 each. The company further decided to utilize the balance of the security premium of Rs. 2,00,000 by issuing fully paid bonus shares. Give journal entries in the books of the company and show necessary workings. 10
Ans: The journal entries for the given transactions in the books of Sky Ltd. are as follows:
To transfer Rs. 4,00,000 from General Reserve to Share Capital (Final Call):
General Reserve A/c Dr. 4,00,000
To Share Capital A/c 4,00,000
(Being bonus declared by paying the final call)
To record the payment of the final call:
Share Capital A/c Dr. 4,00,000
To Bank A/c 4,00,000
(Being the final call payment received)
To transfer Rs. 2,00,000 from Securities Premium to Share Capital (Bonus Issue):
Securities Premium A/c Dr. 2,00,000
To Share Capital A/c 2,00,000
(Being bonus shares issued)
Working:
Number of shares eligible for bonus issue = (Security Premium balance) / (Face value of share)
= Rs. 2,00,000 / Rs. 10
= 20,000 shares
Bonus shares issued = Number of shares eligible for bonus issue
= 20,000 shares
To record the issue of bonus shares:
Share Capital A/c Dr. 2,00,000
To Equity Share Capital A/c 2,00,000
(Being bonus shares issued)
Working:
Face value of bonus shares issued = Face value of original shares
= Rs. 10 per share
Number of bonus shares issued = (Bonus shares issued) / (Face value of share)
= Rs. 2,00,000 / Rs. 10
= 20,000 shares
Therefore, the total number of shares outstanding after the issue of bonus shares = (Original number of shares) + (Bonus shares issued)
= 1,00,000 shares + 20,000 shares
= 1,20,000 shares
Note: The above journal entries and workings are based on the assumption that the company has sufficient General Reserve and Securities Premium balance. If the balance is not sufficient, the company may have to transfer a part of the balance or issue bonus shares in proportion to the available balance.
(6) Write the meaning of holding company. State the principles of consolidation of accounts followed by a holding company. 2+8=10
Ans: A holding company is a company that owns a controlling interest in one or more subsidiary companies. It is primarily engaged in holding and managing investments in subsidiary companies, and does not usually engage in producing goods or services directly. The primary purpose of a holding company is to own and control other companies for strategic and financial purposes.
Principles of consolidation of accounts followed by a holding company:
1.Control: The holding company must have control over the subsidiary company. This means that it has the power to direct the financial and operating policies of the subsidiary and can significantly influence its decision-making process.
2.Common control: The holding company must have a common controlling interest in the subsidiary. This means that the holding company must have a controlling interest in the subsidiary and have a significant influence on the decision-making process.
3.Accounting period: The holding company and subsidiary must have the same accounting period. This is to ensure that the financial statements of the subsidiary can be easily consolidated with those of the holding company.
4.Consistent accounting policies: The holding company must ensure that the subsidiary follows consistent accounting policies. This is to ensure that the financial statements of the subsidiary can be easily consolidated with those of the holding company.
5.Elimination of intercompany transactions: The holding company must eliminate intercompany transactions between itself and the subsidiary. This is to avoid double-counting of transactions and to ensure that the consolidated financial statements reflect the true financial position of the group.
6.Goodwill: Goodwill arising on consolidation must be accounted for in accordance with the accounting standards. Goodwill represents the excess of the cost of the investment over the fair value of the net assets acquired.
7.Minority interest: Minority interest in the subsidiary must be accounted for in accordance with the accounting standards. Minority interest represents the portion of the subsidiary's equity that is not owned by the holding company.
(7) The following ledger balances are extracted from the books of Sun Ltd. on 31/03/2022:
You are required to prepare a Balance Sheet of the company as per schedule III of Companies Act, 2013.
(8) Explain the conditions to be satisfied under section 68 of the Companies Act, 2013 for buyback of shares.
Ans: Section 68 of the Companies Act, 2013 lays down the conditions to be satisfied for the buyback of shares by a company. The following are the conditions that must be satisfied:
Authorization: The buyback must be authorized by the company's articles of association and approved by the board of directors and shareholders by way of a special resolution.
Sources of funds: The buyback must be financed only through the company's free reserves or securities premium account or the proceeds of any earlier issue of shares.
Limit on buyback: The company cannot buy back more than 25% of its total paid-up share capital and free reserves. In addition, the company cannot exceed the maximum amount of buyback specified in the special resolution.
Timeframe: The buyback must be completed within 12 months from the date of the special resolution. The company must also not make another buyback offer within a period of one year from the date of the completion of the buyback.
Modes of buyback: The buyback can be carried out through a tender offer or through the open market route.
Disclosure: The company must disclose the details of the buyback, such as the number of shares bought back, the price paid, and the percentage of share capital bought back, in its financial statements.
Debt-equity ratio: The debt-equity ratio of the company after the buyback must not exceed 2:1. The debt-equity ratio is the ratio of the company's long-term debt to its equity.
By satisfying the conditions laid down under Section 68 of the Companies Act, 2013, a company can buy back its shares in compliance with the law.
Gauhati University Bcom 2nd Sem Corporate Accounting Solved Question Paper 2022
(9) Write five objectives of Amalgamation.
Ans: Amalgamation refers to the process by which two or more companies merge to form a single entity. The following are the five objectives of amalgamation:
1.Diversification: Amalgamation can be used to diversify the product line or geographic reach of the companies involved. By merging with another company, a company can expand its business operations and gain access to new markets and customers.
2.Synergy: Amalgamation can create synergies between the companies involved, resulting in cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved profitability. For example, the merged entity can eliminate duplicate functions, such as administration and marketing, resulting in cost savings.
3.Increased market share: Amalgamation can help companies increase their market share and become more competitive. By merging with another company, a company can gain access to new customers and expand its distribution network.
4.Financial strength: Amalgamation can improve the financial strength of the companies involved. The merged entity can have a stronger balance sheet, greater cash flow, and improved access to capital markets.
5.Improved shareholder value: Amalgamation can result in improved shareholder value. By combining the resources and expertise of the companies involved, the merged entity can generate higher revenues and profits, leading to an increase in shareholder value.
Or
From the following information, calculate the amount of purchase consideration: 5+5=10
East Ltd. is taken over by West Ltd. where East Ltd. is having 60,000 shares of Rs. 10 each. West Ltd. has agreed to discharge the following payments:
(a) Cash payment of Rs. 2 per share of East Ltd.
(b) Issue of 20,000 shares of West Ltd. of Rs. 10 each fully paid at a premium of Rs. 2 per share.
(c) 6% Debentures of Rs. 1,00,000 of East Ltd. will be discharged at 5% premium by the issue of 7% Debentures of West Ltd. at par.
(10) Sunday Ltd. acquired 400 (i.e., 1/4th equity shares of Monday Ltd. of Rs. 100 each on 31/03/2021.
The summarised Balance Sheet of Sunday Ltd. and Monday Ltd. on 31/03/2022 were as under:
Balance Sheet
Monday Ltd. had a credit balance of Rs. 16,000 in the General Reserve and Rs. 8,000 credit balance in Statement of Profit & Loss when Sunday Ltd. acquired the shares in Monday Ltd. Prepare Consolidated Balance Sheet and show necessary workings.
*****
For Complete Solution of Corporate Accounting (Only Theory) Question Paper 2022 Download PDF File 👇
DEMO PDF
Must Visit: GU BCom 2nd Semester NEP FYUGP All Notes, Papers and Solutions Page
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Gauhati University Corporate Accounting Solved Question Paper 2022 is a helpful resource for students to understand and practice corporate accounting. By going through the solutions carefully, students can improve their knowledge and feel more confident for their exams. Keep studying, and good luck with your preparation. You can do it!

![GU Corporate Accounting Solved Question Paper 2022 [Gauhati University BCom 2nd Semester]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjD1qn4ci1kNAegCCOOYnhWmtEeZQWDaxRPHPMI8Sza6otpxbKKzx_m3fIvHBzGpdQff2OzCOn6QHLvYPZvvK8qOj74qBA_x5WJoWVTflofMmot7v467ssZg-j2dcVcvP0GZ-zUTCq8DgFOWDaFEDAFFj4G1WTT5ZqpWhzR0o_TCgot7Ehb0mlRpyl-696v/w200-h200-p-k-no-nu/GU%20Corporate%20Accounting%20Solved%20Paper%202022.jpg)