In this post we have Shared Gauhati University Management Accounting Question Paper Solution 2022 Pdf, B.Com 5th Sem GU, Which can be very beneficial for your upcoming exam preparation. So read this post from top to bottom and get familiar with the question paper solution .
Management Accounting Solved Question Paper
2022
Gauhati University B.Com 5th Sem CBCS Pattern
2022
COMMERCE
(Honours Elective)
Paper: COM-HE-5016)
(Management Accounting)
Full Marks: 80
Time: Three hours
The figures in the margin indicate full marks for the questions.
Answer the following questions: (any ten) 1x10=10
(a) Management Accounting deals with both quantitative and qualitative information.
(Fill in the blank)
(b) Management Accounting is helpful in increasing profitability. (State whether the statement is True or False)
Ans:- False.
(c) Define the term 'Management Accounting'.
Ans:- Management Accounting is the process of identifying, measuring, analyzing, interpreting, and communicating financial and non-financial information to assist management in making informed decisions for achieving the organization's goals and objectives.
(d) Financial statements are
(i) estimates of facts
(ii) anticipated facts
(iii) recorded facts
(iv) All of the above
(Choose the correct answer)
(e) Financial statements are only historical reports. (Fill in the blank)
(f) Debt-equity ratio is the relationship between outsiders' funds and owner's funds. (Fill in the blank)
(g) What is gross profit ratio ?
Ans:- The gross profit ratio is the ratio of gross profit to net sales, expressed as a percentage. It measures the profitability of a company's core operations.
(h) What do you mean by cash budget?
Ans:- A cash budget is a financial planning tool that outlines the expected cash inflows and outflows of an organization over a specific period, typically a month or a year. It helps in managing cash flow effectively.
(i) Labour cost variance is the difference between standard cost of Inbour and actual cost of labour. (Fill in the blank)
(j) State the meaning of standard costing.
Ans:- Standard costing is a cost accounting technique that involves setting predetermined standards for various costs and then comparing actual costs to these standards to analyze variances. It helps in cost control and performance evaluation.
(k) What is break-even point. 2
Ans:- The break-even point is the level of sales at which a company's total revenues equal its total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss.
(l) Marginal costing is a technique of cost control. (State whether the statement is True or False)
Ans:- False.
(m) Contribution is the difference between sales and variable costs. (Fill in the blank)
(n) What is margin of safety?
Ans:- Margin of safety is the difference between the expected or budgeted sales and the break-even sales. It represents the cushion or safety net available to cover unexpected declines in sales.
(0) Standard cost is a predetermined cost. (Fill in the blank)
(p) Liquidity ratios measure long-term solvency of a concern. (State whether the statement is True or False)
Ans:- False.
(q) Management Accounting provides decisions to the management. (State whether the statement is True or False)
Ans:- True .
(r) Liquid ratio is also known as quick ratio. (Fill in the blank)
2. Write brief answers to the following questions (any five) 2×5=10
(i) Mention two limitations of Management Accounting.
Ans:- Two limitations of Management Accounting:
1. Subjectivity: Management accounting relies on estimates and judgments, which can be subjective and may lead to inaccuracies.
2. Historical Data: It primarily uses historical financial data, which may not always reflect current market conditions or future trends.
(ii) Write two distinctions between Cost Accounting and Management Accounting.
Ans:- Two distinctions between Cost Accounting and Management Accounting:
1. Focus:
- Cost Accounting focuses primarily on tracking and controlling costs related to production, while Management Accounting provides a broader view, including planning, decision-making, and performance evaluation.
2. Users:
- Cost Accounting is mainly used by internal parties like production managers, while Management Accounting serves both internal (managers) and external (investors, creditors) stakeholders.
(iii) State two objectives statement analysis.
Ans:- Two objectives of financial statement analysis:
1. Assessing Financial Health: To determine the financial stability and solvency of a company by analyzing its balance sheet and cash flow statement.
2. Performance Evaluation: To evaluate the company's profitability, efficiency, and overall performance through income statement analysis.
(iv) State two advantages of ratio analysis.
Ans:- Two advantages of ratio analysis:
1. Comparison: It allows for easy comparison of a company's financial performance with industry benchmarks and competitors.
2. Quick Assessment: Ratios provide a quick overview of a company's financial health and can highlight areas that need attention.
(v) Mention two distinctions between fixed budget and flexible budget.
Ans:- Two distinctions between fixed budget and flexible budget:
1. Nature:
- Fixed Budget remains unchanged regardless of actual activity levels, while Flexible Budget adjusts based on actual activity levels.
2. Use:
- Fixed Budget is typically used for long-term planning, while Flexible Budget is more suitable for performance evaluation and short-term decision-making.
(vi) Write two limitations of budgetary control.
Ans:- Two limitations of budgetary control:
1. Rigidity: Budgets can be inflexible and may not adapt well to unexpected changes or dynamic business environments.
2. Unrealistic Expectations: Setting overly ambitious budget targets can demotivate employees and lead to unrealistic expectations.
(vii) State the meaning of materials cost variance.
Ans:- Meaning of materials cost variance:
Materials cost variance is the difference between the actual cost of materials used in production and the standard cost of materials allowed, reflecting how efficiently or inefficiently materials were managed and utilized.
(viii) Write the significance of the term. 'variance' in standard costing.
Ans:- Significance of the term 'variance' in standard costing:
Variance in standard costing refers to the difference between actual performance and the predetermined standards. Analyzing variances helps identify areas where actual performance deviates from expectations, enabling managers to take corrective actions.
(ix) State the meaning of marginal costing.
Ans:- Meaning of marginal costing: Marginal costing is a costing technique where only variable manufacturing costs (direct materials, direct labor, and variable overhead) are considered as product costs, while fixed costs are treated as period costs. It is often used for decision-making and contribution margin analysis.
(x) What is angle of incidence in marginal costing ?
Ans:- Angle of incidence in marginal costing: The angle of incidence in marginal costing refers to the point where the total sales revenue equals the total variable costs, resulting in zero contribution margin and zero profit. Beyond this point, any additional sales contribute to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
3. Answer the following questions: (any four) 5×4=20
(i) Mention five objectives of Management Accounting.
Ans:- Five objectives of Management Accounting:
1. Planning: Management accounting helps in the formulation of business plans and budgets by providing relevant financial information. It assists in setting financial goals and developing strategies to achieve them.
2. Controlling: It aids in controlling and monitoring the performance of various departments and activities within an organization. Management accountants use budgets and performance reports to identify variances and take corrective actions as needed.
3. Decision-Making: Management accounting provides valuable data and analysis to support decision-making processes. It helps management make informed choices regarding pricing, product mix, investment opportunities, and cost reduction initiatives.
4. Performance Evaluation: Management accounting helps evaluate the performance of individuals, departments, and the organization as a whole. Key performance indicators (KPIs) and performance reports are used to assess whether objectives are being met.
5. Cost Determination: One of the primary objectives of management accounting is to determine the cost of products, services, and activities accurately. This information is crucial for setting prices, cost control, and profitability analysis.
(ii) Briefly explain the importance and need of Management Accounting.
Ans:- Importance and need of Management Accounting:
1. Informed Decision-Making: Management accounting provides managers with relevant financial and non-financial information, enabling them to make informed decisions. This is crucial for the long-term success of the organization.
2. Performance Evaluation: It helps in evaluating the performance of various aspects of the organization, such as product lines, departments, or projects. This aids in identifying areas for improvement and optimizing resource allocation.
3. Cost Control: Management accounting assists in tracking and controlling costs, which is essential for maintaining profitability. It helps in identifying cost drivers and implementing cost-saving measures.
4. Strategic Planning: Management accounting supports strategic planning by providing data for forecasting, budgeting, and setting goals. It helps align the organization's activities with its long-term objectives.
5. Accountability: It establishes accountability within the organization by measuring the performance of individuals and departments against predetermined targets and standards.
6. Resource Allocation: By providing insights into the profitability and performance of different segments of the business, management accounting helps in allocating resources efficiently.
7. Compliance and Reporting: It ensures compliance with financial regulations and provides data for financial reporting to external stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies.
(iii) Write a brief note on comparative statements.
Ans:- Comparative statements: Comparative statements are financial statements that provide a comparison of financial data for multiple periods. These statements are typically prepared for consecutive accounting periods, such as months, quarters, or years, and are used to analyze the financial performance and position of an organization over time. Comparative statements commonly include:
1. Comparative Income Statement: This statement shows the revenue, expenses, and net income (or net loss) for two or more periods side by side. It allows stakeholders to assess the trends in the company's profitability over time.
2. Comparative Balance Sheet: This statement presents the assets, liabilities, and equity of the organization for multiple periods. It helps in evaluating changes in the company's financial position, including its liquidity and solvency.
3. Comparative Cash Flow Statement: This statement illustrates the cash inflows and outflows for different time periods. It aids in understanding the company's cash management and liquidity trends.
Comparative statements are valuable for financial analysis, as they reveal patterns and changes in an organization's financial performance and position. Analysts use them to identify areas of improvement, assess the impact of management decisions, and make investment or lending decisions.
(iv) Explain in brief the significance of return on capital employed.
Ans:- Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) is a financial metric that measures the efficiency and profitability of a company's capital investments. It is a crucial ratio for both investors and management because it provides insights into how effectively a company is utilizing its capital to generate profits. The significance of ROCE includes:
Performance Assessment: ROCE helps in evaluating the company's overall financial performance. A high ROCE indicates that the company is generating healthy returns on its capital investments, while a low ROCE suggests inefficiency.
Comparison: It allows for easy comparison between companies in the same industry or across different industries. This can assist investors in making informed investment decisions.
Management Effectiveness: ROCE reflects how well a company's management is using its resources to generate profits. It serves as a performance benchmark for management.
Capital Allocation: It aids in decision-making regarding capital allocation. Companies can use ROCE to determine which projects or investments are more profitable and deserving of additional capital.
Risk Assessment: A consistently high ROCE can indicate a lower level of financial risk since the company is generating sufficient returns to cover its costs and provide a return to investors.
(v) State the objectives of budgetary control.
Ans:- The objectives of budgetary control include:
Planning: Budgetary control helps in the planning process by setting specific financial goals and targets for various aspects of the organization, such as sales, expenses, and capital investments.
Resource Allocation: It assists in allocating resources efficiently by ensuring that financial resources are allocated to various departments and projects in a way that aligns with the organization's strategic objectives.
Performance Evaluation: Budgets serve as benchmarks for evaluating the actual performance of the organization. By comparing actual results to budgeted figures, management can identify areas of success and areas that need improvement.
Cost Control: Budgets help in controlling costs and identifying cost overruns. This is vital for maintaining profitability and financial stability.
Communication: Budgets provide a means of communicating financial goals and objectives throughout the organization. They ensure that all employees are aware of their responsibilities in achieving these goals.
Motivation: Budgets can serve as motivational tools for employees. When employees are involved in the budgeting process and have clear targets to achieve, it can enhance their performance and commitment to the organization's goals.
(vi) Briefly explain any five advantages of cash budget.
Ans:- Five advantages of cash budgeting are:
Cash Management: Cash budgets help in managing the company's cash flows effectively. They enable organizations to anticipate periods of cash surplus or deficit, allowing for better management of funds.
Financial Planning: Cash budgets are an integral part of the overall financial planning process. They help in setting financial goals and provide a roadmap for achieving them.
Risk Identification: By forecasting cash flows, organizations can identify potential cash shortages and take proactive measures to address them, reducing financial risk.
Decision Making: Cash budgets provide valuable information for decision-making. They help in evaluating the feasibility of investments, determining the need for external financing, and making informed financial decisions.
Performance Evaluation: Comparing actual cash flows to the budgeted figures allows organizations to assess their financial performance. This evaluation can lead to adjustments in financial strategies and operations to meet objectives more effectively.
(vii) Explain the possible causes for material price variance in standard costing.
Ans:- Possible Causes for Material Price Variance in Standard Costing:
Material price variance is a component of variance analysis used in standard costing to assess the difference between the actual cost of materials purchased and the standard cost of materials allowed for production. It helps organizations identify the reasons for cost deviations and take corrective actions. Several factors can contribute to material price variances:
Changes in Supplier Prices: If the prices charged by suppliers for raw materials change, it can lead to material price variances. This could be due to factors such as inflation, negotiation outcomes, or changes in suppliers.
Quality of Materials: Variations in the quality of materials received can affect their prices. Substandard materials might be available at a lower price but can result in higher processing costs or lower-quality products.
Bulk Purchases: Buying materials in bulk can sometimes lead to favorable prices, reducing the material price variance. Conversely, purchasing materials in smaller quantities may result in higher prices.
Market Conditions: Changes in market conditions, such as supply and demand fluctuations, can impact material prices. Events like natural disasters or geopolitical tensions can also affect material prices.
Currency Exchange Rates: If an organization purchases materials from international suppliers, fluctuations in exchange rates can lead to material price variances.
Contractual Agreements: Long-term contracts with suppliers may have price adjustment clauses based on specific factors, such as inflation rates or changes in market conditions.
Transportation Costs: Variations in transportation costs, including fuel prices and shipping expenses, can affect the overall material price.
Quality Control and Inspection: Quality control measures can influence material prices. Higher-quality materials may cost more but can lead to cost savings in the production process.
Volume Discounts: Large orders or repeat purchases may result in volume discounts, reducing material costs.
Negotiation Skills: Effective negotiation skills can lead to better pricing agreements with suppliers, reducing material prices.
(viii) Write a brief note on cost-volume- profit analysis.
Ans:- Brief Note on Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis:
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis is a financial management tool used by businesses to understand the relationship between sales volume, costs, and profits. It is especially valuable for decision-making and planning. Here's a brief overview:
Components of CVP Analysis:
Costs: CVP analysis categorizes costs into fixed and variable. Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production or sales volume, while variable costs change in direct proportion to changes in production or sales.
Sales Revenue: This represents the total income generated from selling a certain quantity of goods or services.
Contribution Margin: It is the difference between total sales revenue and variable costs. The contribution margin per unit is the amount available to cover fixed costs and contribute to profits.
Key Concepts in CVP Analysis:
Break-Even Point: The break-even point is the level of sales at which total revenue equals total costs, resulting in zero profit. It helps a business understand when it will start making a profit.
Margin of Safety: The margin of safety is the difference between actual sales and the break-even point. It indicates how much sales can drop before the company incurs losses.
Profit-Volume (P-V) Graphs: P-V graphs visually represent the relationship between costs, revenues, and profits, helping businesses analyze different scenarios and make informed decisions.
Target Profit Analysis: CVP analysis can be used to determine the level of sales required to achieve a specific profit target.
Benefits of CVP Analysis:
Decision-Making: CVP analysis aids in decisions related to pricing, product mix, production levels, and cost control.
Risk Assessment: It helps assess the impact of various factors, such as changes in costs or sales volume, on profitability.
Financial Planning: CVP analysis is crucial for budgeting and forecasting future financial performance.
4. Answer the following questions: (any four) 10×4=40
(a) Management Accounting is the presentation of accounting information in such a way as to assist management in the creation of policy and in the day-to-day operations of the undertakings.' Explain this statement.
Ans:- The statement "Management Accounting is the presentation of accounting information in such a way as to assist management in the creation of policy and in the day-to-day operations of the undertakings" can be broken down and explained as follows:
1. Presentation of Accounting Information: Management accounting involves the collection, analysis, and presentation of financial and non-financial information relevant to an organization. This information is derived from various sources within the company, including financial statements, budgets, forecasts, and operational data.
2. Assisting Management: The primary purpose of management accounting is to provide support and aid to the management team of an organization. It is distinct from financial accounting, which is primarily concerned with reporting to external stakeholders like shareholders, regulators, and creditors. Management accounting, on the other hand, focuses on serving the needs of internal management.
3. Creation of Policy: Management accounting helps in the formulation of policies and strategies for the organization. By providing data and analysis, it assists managers in making informed decisions about the direction the company should take. For example, it can help in deciding pricing strategies, product mix, and investment decisions.
4. Day-to-Day Operations: Management accounting is not just about long-term strategic decisions. It also plays a crucial role in the day-to-day operations of the company. Managers need real-time or periodic information to monitor performance, control costs, and make adjustments as necessary. Management accountants provide this information in a format that is easy for managers to understand and use.
how management accounting achieves these objectives:
- Customized Reporting: Management accountants tailor reports to suit the specific needs of different levels of management. Top-level executives may need high-level summaries and strategic insights, while middle managers require more detailed operational data.
- Cost Analysis : Management accountants often focus on analyzing costs to help management identify areas where cost reductions or efficiency improvements can be made.
- Budgeting and Forecasting : They assist in the creation and monitoring of budgets and forecasts, which are essential for planning and control.
- Performance Measurement : Management accountants design key performance indicators (KPIs) and dashboards to assess the performance of various departments and initiatives.
- Scenario Analysis : They may run scenarios and simulations to assess the potential impact of different decisions and strategies.
- Risk Assessment : Management accountants also play a role in identifying and assessing risks associated with various business decisions.
(b) Briefly discuss about cost control and cost reduction. Also explain its advantages. 3+3+4=10
Ans:- Cost Control and Cost Reduction:
Cost Control:
Cost control refers to the management's efforts to regulate and restrain costs within an organization to ensure they do not exceed budgeted or planned levels. The primary objective of cost control is to maintain cost efficiency and prevent unnecessary expenditures. Here are some key points about cost control:
1. Monitoring and Comparison: Cost control involves monitoring actual costs and comparing them to budgeted costs. This allows organizations to identify areas where costs are exceeding expectations.
2. Variance Analysis: Variance analysis is a crucial tool in cost control. It helps identify the reasons for cost variances and enables corrective actions to be taken when necessary.
3. Budget Adherence: Cost control ensures that the organization adheres to its budget and allocates resources efficiently to achieve its goals.
Advantages of Cost Control:
- Helps in maintaining financial discipline within the organization.
- Ensures that resources are used efficiently and effectively.
- Enables better decision-making by providing insights into cost trends.
- Helps in stabilizing prices of products or services, which can be beneficial for customers and stakeholders.
Cost Reduction:
Cost reduction involves strategies and actions aimed at reducing the overall expenses incurred by an organization without compromising the quality of its products or services. Cost reduction is often a more proactive approach to managing expenses compared to cost control. Here are some key points about cost reduction:
1. Process Improvement: Cost reduction may involve streamlining processes, increasing efficiency, and eliminating waste to lower production or operational costs.
2. Negotiating with Suppliers: Negotiating better terms with suppliers, such as bulk discounts or longer payment terms, can help reduce procurement costs.
3. Automation and Technology: Implementing technology and automation can lead to cost reductions by reducing labor costs and increasing productivity.
Advantages of Cost Reduction:
- Increased profitability: Lower costs can lead to higher profit margins.
- Competitive advantage: Reduced costs can allow an organization to offer lower prices to customers, gaining a competitive edge.
- Better resource allocation: By cutting unnecessary expenses, resources can be allocated to more critical areas of the business.
- Improved financial stability: Cost reduction efforts can enhance an organization's financial health and resilience.
(c) Explain the procedure of analysis and interpretation of financial statements. Also discuss the limitations of financial analysis. 5+5=10
Ans:- Analysis and Interpretation of Financial Statements:
Procedure of Analysis and Interpretation:
1. Gather Financial Statements: The first step is to collect the financial statements of the company, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
2. Calculate Financial Ratios: Financial ratios are computed using data from the financial statements to assess various aspects of a company's performance. Common ratios include profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and leverage ratios.
3. Comparative Analysis: Compare the current financial data with historical data and industry benchmarks to identify trends, anomalies, and areas of concern.
4. Common-Size Analysis: Convert financial statement line items into percentages of total assets (for the balance sheet) or total revenue (for the income statement). This helps in understanding the relative composition of various accounts.
5. Trend Analysis: Analyze changes in financial data over time to identify patterns and assess the direction in which the company is heading.
6. Ratio Analysis: Interpret the calculated financial ratios to evaluate the company's financial health, profitability, liquidity, and efficiency.
7. Cash Flow Analysis: Examine the cash flow statement to understand the company's ability to generate cash and its liquidity position.
Limitations of Financial Analysis:
1. Historical Data: Financial analysis relies on historical data, which may not accurately reflect future performance or changes in the business environment.
2. Subjectivity: Interpretation of financial data can be subjective and influenced by the analyst's assumptions and biases.
3. Limited Scope: Financial statements may not capture all relevant information, such as non-financial factors like market trends, competition, and management quality.
4. Comparability Issues: Comparing financial data across companies can be challenging due to differences in accounting methods and industry norms.
5. Manipulation: Financial statements can be manipulated or misrepresented, leading to inaccurate analysis.
6. No Guarantee of Success: Even if financial analysis indicates favorable results, it does not guarantee a company's success or future profitability.
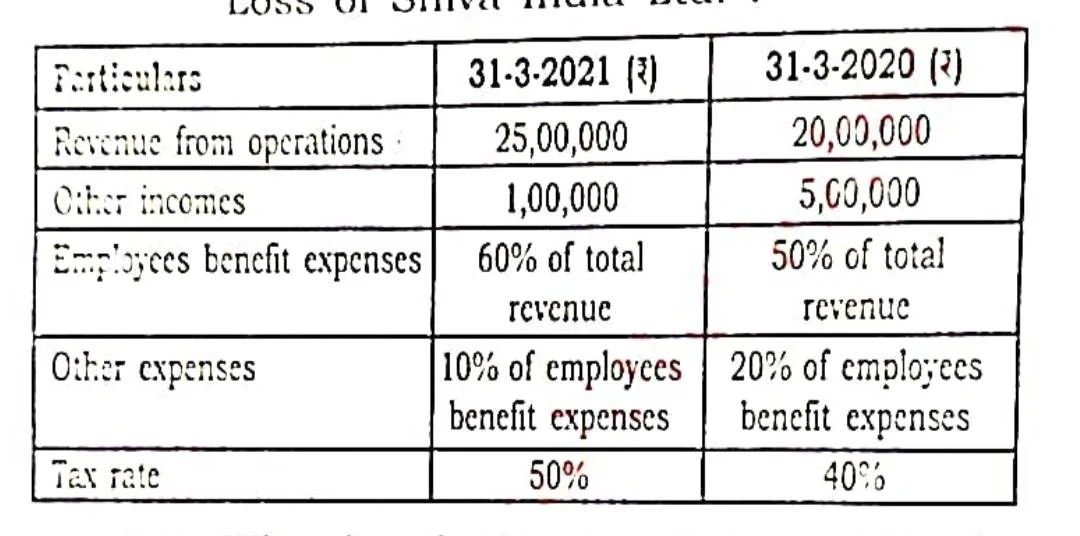
(d) From the following data, prepare a Comparative Statement of Profit and Loss of Shiva India Ltd.:
(e) What is a budget? Briefly explain the advantages of budgetary control. 2+8=10
Ans:- A budget is a financial plan that outlines an organization's or individual's expected income and expenses over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year. It serves as a roadmap for managing and allocating resources to achieve financial goals.
Advantages of budgetary control:
Financial Planning: Budgets help organizations plan their finances by setting clear financial goals and targets. This enables them to allocate resources efficiently and allocate funds to various departments or projects as needed.
Resource Allocation: Budgets provide a framework for allocating resources such as funds, labor, and materials to different activities. This ensures that resources are used effectively and that the organization's priorities are met.
Performance Evaluation: Budgetary control allows for regular monitoring and comparison of actual financial performance against the budgeted figures. It helps identify deviations and take corrective actions if necessary.
Cost Management: Budgets help in controlling costs by setting limits and guidelines for spending. This can lead to cost reduction and improved profitability.
Goal Setting: Budgets help organizations set specific financial goals and objectives, which can motivate employees and departments to work towards achieving these targets.
Communication and Coordination: Budgets serve as a means of communication between different levels of management and departments within an organization. It encourages coordination and collaboration among various teams to achieve common financial objectives.
Decision Making: Budgets provide valuable information for decision-making. They help in evaluating the financial feasibility of projects and initiatives, allowing organizations to make informed choices about resource allocation.
Performance Accountability: Budgets create a system of accountability within an organization. Managers and employees are held responsible for adhering to the budget and achieving the set financial goals.
(f) X & Co. wishes to arrange overdraft facilitics with bankers during the period April to June of a particular year, when it will be manufacturing mostly for stock. Prepare a cash budget for the above period from the following data, indicating the extent of the bank facilities, the company will require at the end of each month:
Other informations :
(i) 50% of the credit sales are realised in the month following the sales and the remaining sales in second month following.
(ii) Creditors are paid in the following month of purchase.
(iii) Cash at bank is 25,000 on 1st April.
Ans:-
Here's how the calculations were done for each month:
April:
Collections from February sales (50%): 1,80,000 * 0.50 = 90,000
Collections from March sales (50%): 1,92,000 * 0.50 = 96,000
Total Collections: 90,000 + 96,000 = 1,86,000
Net Cash Flow: Collections - Wages - Purchases - Payments to Creditors = 1,86,000 - 2,43,000 - 11,000 - 11,000 = -2,02,000
Cash at Bank: Cash at Bank on April 1st + Net Cash Flow = 25,000 + (-2,02,000) = 23,000
May:
Collections from April sales (50%): 1,08,000 * 0.50 = 54,000
Collections from February sales (remaining 50%): 1,80,000 * 0.50 = 90,000
Total Collections: 54,000 + 90,000 = 1,44,000
Net Cash Flow: Collections - Wages - Purchases - Payments to Creditors = 1,44,000 - 2,46,000 - 10,000 - 10,000 = -1,05,000
Cash at Bank: Cash at Bank on April 30th + Net Cash Flow = 23,000 + (-1,05,000) = 1,000
June:
Collections from May sales (50%): 1,74,000 * 0.50 = 87,000
Collections from March sales (remaining 50%): 1,92,000 * 0.50 = 96,000
Total Collections: 87,000 + 96,000 = 1,83,000
Net Cash Flow: Collections - Wages - Purchases - Payments to Creditors = 1,83,000 - 2,68,000 - 15,000 - 15,000 = -1,29,000
Cash at Bank: Cash at Bank on May 31st + Net Cash Flow = 1,000 + (-1,29,000) = -1,28,000
(g) (i) Explain wage rate variance and labour efficiency variance. 2+2=4
Ans:- Wage rate variance and labor efficiency variance are two components of labor variances used in variance analysis, a managerial accounting technique. These variances help organizations assess and understand the reasons for differences between budgeted (expected) and actual labor costs.
Wage Rate Variance:
Definition: Wage rate variance, also known as rate variance or rate of pay variance, measures the difference between the actual wage rate paid to employees and the budgeted (standard) wage rate for a specific period.
Formula: Wage Rate Variance = (Actual Wage Rate - Standard Wage Rate) × Actual Hours Worked
Interpretation:
A positive wage rate variance occurs when the actual wage rate paid is higher than the standard rate. This suggests that employees were paid more per hour than expected.
A negative wage rate variance occurs when the actual wage rate paid is lower than the standard rate, indicating cost savings in labor.
Labor Efficiency Variance:
Definition: Labor efficiency variance, also known as efficiency variance or quantity variance, measures the difference between the actual hours worked and the standard hours allowed for the actual level of production.
Formula: Labor Efficiency Variance = (Actual Hours Worked - Standard Hours Allowed) × Standard Wage Rate
Interpretation:
A positive labor efficiency variance occurs when employees take more time to complete tasks (more hours worked) than what was expected. This implies inefficiency in labor usage.
A negative labor efficiency variance occurs when employees complete tasks more quickly (fewer hours worked) than expected, indicating efficient use of labor.
(ii) From the following information regarding a standard product, calculate labour variances: 6
Labour rate - 50 paise per hour
Hours per unit - 10 hours:
Units produced - 500
Hours worked - 6000
Actual labour cost - 22,400
Ans:- To calculate labor variances, you can use the following formulas:
1. Labor Rate Variance = (Actual Hours Worked × Actual Rate) - (Actual Hours Worked × Standard Rate)
2. Labor Efficiency Variance = (Standard Rate × Actual Hours Worked) - (Standard Rate × Standard Hours for Actual Production)
Given the information provided:
- Labor rate = 50 paise per hour (0.50 INR per hour)
- Hours per unit = 10 hours
- Units produced = 500
- Hours worked = 6000
- Actual labor cost = 22,400 INR
First, calculate the standard hours for actual production:
Standard Hours for Actual Production = Units Produced × Hours per Unit
Standard Hours for Actual Production = 500 units × 10 hours/unit = 5000 hours
Now, calculate the labor rate variance:
Labor Rate Variance = (Actual Hours Worked × Actual Rate) - (Actual Hours Worked × Standard Rate)
Labor Rate Variance = (6000 hours × 0.50 INR/hour) - (6000 hours × 0.50 INR/hour)
Labor Rate Variance = (3000 INR) - (3000 INR)
Labor Rate Variance = 0 INR
Next, calculate the labor efficiency variance:
Labor Efficiency Variance = (Standard Rate × Actual Hours Worked) - (Standard Rate × Standard Hours for Actual Production)
Labor Efficiency Variance = (0.50 INR/hour × 6000 hours) - (0.50 INR/hour × 5000 hours)
Labor Efficiency Variance = (3000 INR) - (2500 INR)
Labor Efficiency Variance = 500 INR
So, the labor rate variance is 0 INR, and the labor efficiency variance is 500 INR.
(h) (i) State the steps standard involved in costing. 4
Ans:- Standard costing is a widely used cost accounting technique that helps businesses establish predetermined, expected costs for products or services. It involves comparing actual costs with predetermined standards to evaluate performance and make informed decisions. Here are the steps typically involved in standard costing:
1. Establish Standard Costs:
- Determine the standard cost for each cost component, such as direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. These standards are typically based on historical data, industry benchmarks, or engineering estimates.
2. Create a Standard Cost Card:
- Develop a standard cost card for each product or process, listing the standard quantities and prices for materials, labor rates, and overhead rates. This card serves as a reference point for cost comparisons.
3. Record Actual Costs:
- Throughout the accounting period, record actual costs incurred in producing goods or providing services. Actual costs can vary due to changes in factors like material prices, labor efficiency, and overhead expenses.
4. Calculate Variances:
- Calculate the cost variances by comparing actual costs to the standard costs. Variances are typically classified as:
- Material Price Variance: Difference between the actual material cost and the standard material cost.
- Material Usage Variance: Difference between the actual material usage and the standard material usage.
- Labor Rate Variance: Difference between the actual labor rate and the standard labor rate.
- Labor Efficiency Variance: Difference between the actual labor hours worked and the standard labor hours.
- Overhead Variance: Difference between actual overhead costs and applied overhead costs.
5. Analyze Variances:
- Investigate the reasons for cost variances. Positive variances (favorable) suggest cost savings, while negative variances (unfavorable) indicate cost overruns. Identifying the root causes helps in taking corrective actions.
6. Report and Interpret Results:
- Prepare variance reports that provide insights into the performance of different departments or processes. Managers use these reports to make informed decisions and take corrective actions if necessary.
7. Adjust Standard Costs (if needed):
- If significant and recurring variances occur due to changes in business conditions, revise the standard costs to better reflect the new cost expectations.
(ii) Discuss the limitations of standard costing.
Ans:- Limitations of Standard Costing:
1. Assumes Static Conditions:
- Standard costing assumes that conditions remain constant, which may not be the case in rapidly changing environments. Economic fluctuations, price changes, and other factors can render standard costs obsolete.
2. Rigidity:
- Standard costing can lead to inflexibility in decision-making since it relies on predetermined standards. It may not account for innovative changes in production methods or materials.
3. Overemphasis on Variances:
- Excessive focus on variances can lead to neglect of other important factors affecting performance, such as quality, customer satisfaction, and long-term strategic goals.
4. Difficulty in Setting Accurate Standards:
- Setting accurate standards can be challenging, as it requires predicting future conditions. Inaccurate standards can lead to misleading performance evaluations and decisions.
5. Labor-Intensive:
- The process of maintaining standard costs and analyzing variances can be labor-intensive and costly, particularly in organizations with complex operations.
6. Ignores Non-Financial Measures:
- Standard costing primarily focuses on financial metrics, ignoring non-financial measures like customer satisfaction or employee morale, which are crucial for long-term success.
(i) Explain the advantages of marginal costing and cost-volume-profit analysis.
Ans:- Marginal costing and cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis are essential tools in managerial accounting that offer several advantages for businesses:
Advantages of Marginal Costing:
1. Simple and Easy to Understand: Marginal costing is straightforward and easy to comprehend. It segregates costs into fixed and variable components, making it simpler for managers to analyze cost behavior and make decisions.
2. Helps in Pricing Decisions: Marginal costing provides insights into the incremental cost of producing additional units, making it valuable for pricing decisions. Managers can set prices based on the marginal cost to ensure profitability.
3. Contribution Margin Analysis: It calculates the contribution margin, which is the difference between sales revenue and variable costs. This helps identify the portion of revenue that contributes towards covering fixed costs and generating profit.
4. Useful for Break-Even Analysis: Marginal costing is instrumental in determining the break-even point—the level of sales at which total revenue equals total costs. This aids in assessing the minimum level of sales required to cover fixed costs.
5. Facilitates Cost Control: By focusing on variable costs, marginal costing allows managers to control and reduce costs more effectively. Identifying cost variations helps in cost control efforts.
Advantages of Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis:
1. Profit Planning and Forecasting: CVP analysis enables businesses to plan and forecast profits at various levels of sales and production. This helps in setting achievable targets and strategies.
2. Break-Even Analysis: CVP analysis provides a clear understanding of the break-even point, which is crucial for decision-making. Managers can assess the risk associated with different sales levels.
3. Sensitivity Analysis: Businesses can use CVP analysis to assess the impact of changes in variables such as selling price, variable costs, or fixed costs on profits. This helps in scenario planning and risk management.
4. Decision-Making Support: CVP analysis aids in various decisions, such as pricing, product mix, and production volume. It helps managers make informed choices that align with their financial objectives.
5. Performance Evaluation: CVP analysis can be used to evaluate the performance of different products, departments, or divisions within an organization. By analyzing contribution margins, managers can allocate resources more effectively.
6. Capital Budgeting: CVP analysis is useful in evaluating the financial feasibility of capital investment projects. It helps assess how an investment will impact the company's profitability and break-even point.
(j) Assuming that the cost structure and selling prices remain same in period and II, find out -
Ans:- To find out how changes in sales affect profit when the cost structure and selling prices remain the same between two periods (I and II), you can calculate the profit margin in each period and then analyze the difference.
The profit margin is calculated using the following formula:
Profit Margin (%) = (Profit / Sales) x 100
Let's calculate the profit margin for both periods:
For Period I:
Profit Margin = (9,000 / 1,20,000) x 100 = 7.5%
For Period II:
Profit Margin = (13,000 / 1,40,000) x 100 = 9.29%
Now, let's analyze the difference:
In Period I, the profit margin was 7.5%, and in Period II, it increased to 9.29%. This indicates that the company was able to achieve a higher profit margin in Period II compared to Period I, despite a similar cost structure and selling prices. This suggests that either the company increased efficiency, reduced costs, or improved sales and marketing strategies in Period II, resulting in higher profits for the same level of sales.
-0000-
Also Visit : Gauhati University BCom 5th Sem Question Papers, Solved Papers, PDF & Notes

![Management Accounting Solved Question Paper 2022 PDF [Gauahti University B.Com 5th Sem]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiv3_g79gWcQAHH7IYk20-Z10LLxxx6oVZwMvFjJ90oIiD2mQ1Vn6s8bkhuUMfFTnp9PgX0Wfp_OKnmZ0b2bqkHhow21q5QVFi6hBgJ8YnbjO9vy4TdwiUGX6rJ3fd2bBKbU3jyN6fLtLA0mCD5zvgDZvLhJIvRdQdbIeaVKcqqjZCXAeCo72UDVz5euGuT/w200-h200-p-k-no-nu/Gauhati%20University%20BCom%20Solved%20Question%20paper%20Bcom%205th%20sem%20Management%20Accounting,%20Management%20Accounting%20so...University%20Pdf%20,%20Management%20Accounting%20solved%20question%20paper%20pdf%202022%20,%20Management%20Accounting%20Question%20Paper%20pdf%20download.webp)